Who was John (the Apostle) in the Bible?
Who was John (the Apostle) in the Bible? Have you ever wondered how a simple fisherman became one of the most influential figures in the Christian faith? John the Apostle, often referred to as Saint John, was one such figure.
He was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and is traditionally held to be the author of the Gospel of John, three Epistles of John, and the Book of Revelation. John’s life and works have had a lasting impact on Christianity and the interpretation of the New Testament.
This article delves into the multifaceted role John played within the early Church and the broader biblical canon.
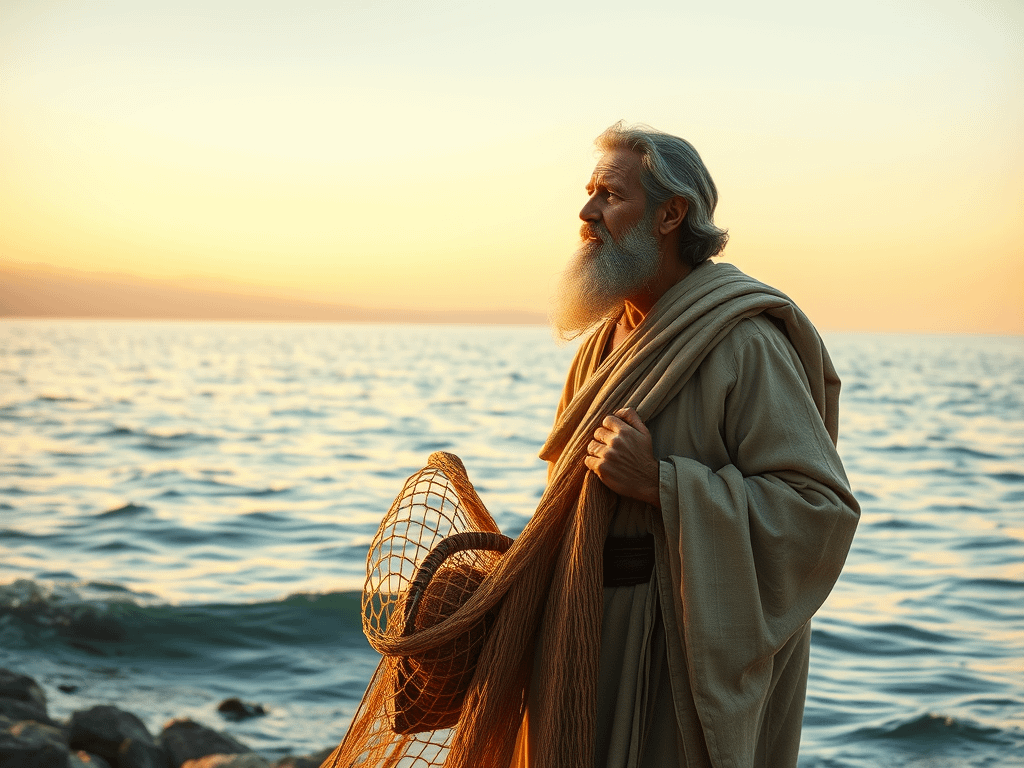
Originating from a humble background, John, the son of Zebedee and Salome, lived in Bethsaida, a town in Galilee. He and his brother James were fishermen before they were called by Jesus to become “fishers of men.”
Known for his close relationship with Jesus, John is often depicted as the disciple whom Jesus loved, highlighting a unique bond that provides insight into the personal dynamics within the group of apostles.
This close relationship afforded John a privileged perspective, which is evident in his writings.
The Role of John in the Early Church
John played a significant role in the early Christian Church, becoming a spiritual leader who guided new converts and reinforced the teachings of Jesus Christ.
He was known for his unwavering faith and courage, traits that were crucial in a time when Christians faced persecution for their beliefs.
| Role | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Leader | Ephesus | Spread Christianity among Gentiles |
| Teacher | Jerusalem | Taught new converts |
| Defender | Asia Minor | Defended Christian doctrine |
| Writer | Patmos | Contributed to New Testament texts |
After the Ascension of Jesus, John remained active in the Church, particularly in Jerusalem, where he reportedly worked alongside Peter. He later moved to Ephesus, where he carried on his mission.
Tradition holds that John lived a long life compared to other apostles, who mostly met violent ends due to martyrdom.
This longevity allowed him to mature spiritually and intellectually, contributing significantly to the early Church’s structure and theology.
John’s Writings and Their Significance
John’s contributions to the New Testament are profound. The Gospel of John differs in tone and content from the Synoptic Gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke.
His Gospel delves deeply into the spiritual and theological aspects of Jesus’s life and mission, emphasizing themes such as light, love, and truth.
In addition to his Gospel, John also authored three Epistles. These letters further illustrate his commitment to spreading the message of love and truth.
John’s epistles address community issues, urging believers to maintain their faith and love amidst rising tensions and false teachings.
“Let us not love with words or speech but with actions and in truth.” – 1 John 3:18
Lastly, the Book of Revelation, attributed to John, presents a prophetic vision of the end times. Rich in symbolic and apocalyptic imagery, this work has been the subject of much interpretation and is considered one of the most mysterious books of the Bible.
John’s Symbolism and Iconography
John has been associated with various symbols and iconography in Christian art and literature. One of the most common symbols is the eagle, representing the heights to which John rises in his theological writings, especially in depicting Jesus as the Son of God.
- The Eagle: symbolizing his high-soaring theological insight.
- A Book: representing his contributions to the biblical canon.
- The Chalice: stemming from a legend where John safely drinks a cup of poison.
- The Serpent: often depicted escaping from a chalice, symbolizing the triumph over evil.
These symbols not only identify John in artistic depictions but also encapsulate his theological contributions and the perceptions held about him in the Christian tradition. His portrayals often emphasize the divine inspiration and wisdom evident in his writings.
Understanding John’s Theological Themes
John’s works are rich in theological themes that continue to resonate deeply within Christian doctrine. Love, in particular, is a recurring motif.
John’s writings emphasize love as a fundamental tenet of faith, reiterating the commandment to love one another as Jesus loved his disciples.
Another key theme is truth. John frequently contrasts light and darkness, using these metaphors to illustrate the struggle between truth and falsehood.
This dualism is present throughout his Gospel and letters, underscoring the importance of living in accordance with divine truth.
Furthermore, John’s portrayal of Jesus is distinctive. His works highlight the divine nature of Christ, focusing on Jesus’s identity as the Word made flesh.
This theological perspective has significantly influenced Christian Christology, encouraging believers to reflect on the nature of divinity and humanity.
John in Art and Literature
John’s profound influence extends beyond theological studies and into the realms of art and literature.
Throughout history, he has been a subject of numerous artistic works, from early Christian mosaics to Renaissance paintings. Artists often depict John alongside Jesus, highlighting their deep connection.
In literature, John’s writings have inspired countless authors and poets who draw on his rich imagery and themes. His exploration of love and divine truth provides a timeless source of inspiration, resonating with both religious and secular audiences.
The depiction of John as a mystic and theologian reflects the broader impact of his works. John’s unique approach to narrating the life and teachings of Jesus has left an indelible mark on Christian thought, illustrating his enduring relevance.
The Legacy of John the Apostle
John the Apostle’s legacy endures in both religious and cultural contexts. As one of the foundational figures of Christianity, his teachings continue to inform and inspire believers around the world.
His theological insights have shaped Christian doctrine, offering invaluable perspectives on the nature of love, truth, and divinity.
John’s life demonstrates the transformation possible through faith. From a fisherman to a beloved disciple, his journey serves as a testament to the power of belief and the strength found in spiritual commitment.
Moreover, his influence is evident in the continued study and veneration of his writings, illustrating the timeless relevance of his teachings.
John’s literary contributions, filled with rich symbolism and profound themes, remain central to understanding the Christian faith.
John’s Feast Days and Commemorations
In recognition of his significance, John is commemorated through various feast days and religious observances. His major feast day, celebrated by many Christian denominations, is December 27th.
This celebration honors John’s contributions to the Church and his extraordinary life as one of Jesus’s closest disciples.
John is also venerated in Eastern Christianity with additional feast days acknowledging his role as an evangelist and theologian.
These commemorations serve to celebrate John’s lasting impact on the faith, offering believers an opportunity to reflect on his teachings and legacy.
Through these observances, John’s influence continues to be celebrated, reinforcing the enduring importance of his works within the Christian tradition.
These celebrations allow believers to connect with John’s spiritual insights, deepening their understanding and appreciation of his contributions.

John’s Influence on Modern Christianity
John’s influence on modern Christianity is profound, shaping both theological perspectives and liturgical practices.
His emphasis on love as the defining characteristic of Christian life continues to guide contemporary Christian ethics.
Churches around the world draw from John’s writings to emphasize the importance of community, compassion, and commitment to truth.
In addition, John’s apocalyptic vision in the Book of Revelation remains a focal point for eschatological studies. His symbolic and prophetic narrative encourages ongoing exploration and interpretation, engaging scholars and believers alike.
John’s work is frequently referenced in modern sermons, theological discussions, and religious education.
His emphasis on spiritual understanding and divine love provides a foundational backdrop for contemporary Christian life, illustrating how the teachings of an apostle from the first century continue to resonate today.
Conclusion
John the Apostle stands as a monumental figure in Christian history, whose life and works continue to inspire and instruct believers around the world.
His contributions to the New Testament have provided profound insights into the life and teachings of Jesus, offering a unique perspective that highlights the divine and eternal nature of Christ.
Whether through his Gospel, his Epistles, or the prophetic Revelation, John’s influence transcends time, speaking to the core tenets of Christian faith.
His legacy endures not only through his writings but also through the lives of those who continue to be moved by his call to love and truth.
As the beloved disciple and a witness to the events that shaped Christianity, John remains an enduring symbol of faith, hope, and the transformative power of the Gospel.
FAQ – Common Questions
Why is John often called “the beloved disciple”?
John is referred to as “the beloved disciple” in the Gospel of John, which highlights his close relationship with Jesus. This title underscores the special bond and trust between them.
What distinguishes John’s Gospel from the Synoptic Gospels?
John’s Gospel focuses more on the spiritual and theological elements of Jesus’s life, rather than just historical events. It emphasizes themes like love, light, and divine truth.
What are the main themes in the Epistles of John?
The Epistles of John emphasize love, truth, and fellowship within the Christian community, while also warning against false teachings and emphasizing the importance of living in accordance with God’s commandments.
How has John’s work influenced Christian theology?
John’s writings have significantly shaped Christian theology, particularly in the areas of Christology and eschatology. His depiction of Jesus as both divine and human has been central to understanding the nature of Christ.
Is there historical evidence for John’s authorship of Revelation?
While traditional attribution credits John with writing Revelation, scholarly debate exists about the authorship. However, early Church writings and tradition strongly associate the text with John the Apostle.